Vitamin A
as 50% beta carotene and as 50% retinyl palmitate
1,500mcg RAE total, 750mcg RAE of each form (Powder/Capsules)
750mcg RAE total (Essentials)
(RAE, retinol activity equivalents, standardizes the dose of Vitamin A between the two forms as their absorption rates differ significantly)
How it supports mama:
- immune function
-
healthy skin and vaginal tissues
-
thyroid function
-
production of hormones like estrogen and progesterone
-
pregnancy viability (embryo implantation)
-
placenta development
-
adequate milk supply
How it supports baby:
-
adequate birth weight
- fetal facial development including ears and eyes
-
full-term gestation
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
Many mamas avoid the “active” forms of Vitamin A, like Retinyl Palmitate.
Why this form?
Retinyl palmitate is an active form that is more readily usable by the body. It is otherwise found in animal foods, especially liver and dairy products.
Beta Carotene is the form of Vitamin A found in plants. It is often poorly absorbed and inefficiently converted into the active (ready-to-be used) form after absorption. And, many women have a genetic variation that prevents the conversion completely.
Why this dose?
The combination provides enough retinyl palmitate to be effective, especially for those that don’t eat enough meat or dairy, or have Beta Carotene conversion difficulty, while still being safe for all mamas and mamas-to-be.


Additional information to note
There is a lot of internet chatter around avoiding active forms of Vitamin A like Retinyl Palmitate in supplements during pregnancy. This caution exists because Vitamin A is a fat soluble nutrient which means that it is not readily eliminated and can bioaccumulate. However, we think instructions to entirely avoid Retinyl Palmitate are misguided. Though toxicity can occur at very high levels*, avoidance of Retinyl Palmitate has led to a high rate of Vitamin A deficiency in pregnancy and in newborns, which can be damaging as well.
*The WHO says 10,000IU (equivalent to 3,000mcg) a day of the active form of Vitamin A is the upper limit. However, other research suggests that no risk has been observed at 30,000IU / 9.000mcg a day. Beta Carotene does not apply towards the upper limit, as there is no research to suggest that Beta Carotene can cause Vitamin A toxicity.
Vitamin C
as Ascorbic Acid
300mg (Powder/Capsules) / 75mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- immune function
- antioxidant - prevents cell damage
- healthy connective tissues and skin (collagen synthesis)
- iron absorption
- mental health as a component of the neurotransmitter norepinephrine
- metabolism and healthy energy levels
How it supports baby:
- immune function
- cell division, i.e. how baby grows
- building cartilage, tendons, bones, teeth, blood vessels, and skin
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
- Degrades quickly after fresh produce is picked and with cooking
- Intake of fruit rich in Vitamin C is reduced due to sugar content concerns
- RDA is grossly inadequate
- Limited amounts in most prenatals
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Ascorbic acid is the main form of Vitamin C found naturally in fruit and other foods.
Why this dose?
This is a highly efficacious dose of Vitamin C to support mama in pregnancy and postpartum as delivery and labor use extraordinary amounts of Vitamin C.


Vitamin D
as D3 Cholecalciferol
4,000IU (Powder/Capsules) / 2,000IU (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- immune function
- calcium and phosphorus absorption
- bind and eliminate toxins
- a healthy inflammatory response
- healthy blood pressure
- a healthy full-term pregnancy
How it supports baby:
- immune function
- cell division, i.e. how baby grows
- forming bones and teeth
- respiratory function
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
50% of women critically deficient* despite taking a prenatal vitamin. 90%+ of women are deficient.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
*Critically deficient defined here as 37.5 -80 nmol/L or less of serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (circulating Vitamin D in the body and the best measure of Vitamin D supply). Many practitioners in our community prefer to see levels closer to 125 - 200 nmol/L (50 - 80 ng/ml) and even in sunny Southern California see deficiency rates upwards of 90% for women that do not appropriately supplement with Vitamin D.
Why this form?
Vitamin D3 is technically not a vitamin, but a prohormone. Prohormones are the building blocks of fully formed hormones. Your skin produces Vitamin D3 when it is exposed to sunlight. But, most mamas don't get enough sun and Vitamin D is difficult to get from food. In addition, many women contain genetic variations that predispose them to lower levels of Vitamin D. Vitamin D3 is more readily used by the body than Vitamin D2.
Why this dose?
Our dose provides enough to be effective, while still being safe for all mamas and mamas-to-be. Most prenatal supplements will add 2,000 IU of Vitamin D3 at most. Through research and clinical practice of our practitioner partners we do not think 2,000 IU is enough. 4,000 IU is more effective and highly safe. As one example, a 2011 well designed placebo and randomized controlled study on Vitamin D3 supplementation in pregnant women evaluated this dose. At 4,000 IU per day 82% of women reached proper blood levels of vitamin D and no participants had side effects of excessive blood levels of Vitamin D3. In addition, women taking 4,000 IU had far lower rates of pregnancy complications compared to those taking a lower dose.


Additional information to note
Additional Vitamin D3 beyond 4,000 IU may be required for some mamas whose levels are especially low.
Vitamin E
as mixed tocopherols from rapeseed
67 mg (30mg as d-alpha tocopherol that can be applied towards Vitamin E claim)
30mg (Powder/Capsules) / 10mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- healthy skin
- anti-aging
- healthy neurological function
- normal cardiac function
- healthy lipid profiles
- normal inflammatory responses
- fertility
How it supports baby:
- healthy neurological function
- normal cardiac function
- promoting healthy lipid profiles
- normal inflammatory response
- healthy body weight
- optimal cognitive development
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
The potent antioxidant properties of Vitamin E benefit women at all stages of mamahood.
1 RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Tocopherols are antioxidants that occur naturally in foods such as nuts, seeds, and leafy green vegetables. We source ours from rapeseed oil rather than the more commonly found soybean oil. We provide 67mg of mixed tocopherols overall, with 30mg from d-alpha tocopherols declared as Vitamin E.
Why this dose?
This dose provides extra antioxidant support to meet the needs of pregnant and nursing mamas. It is also very supportive for conception.


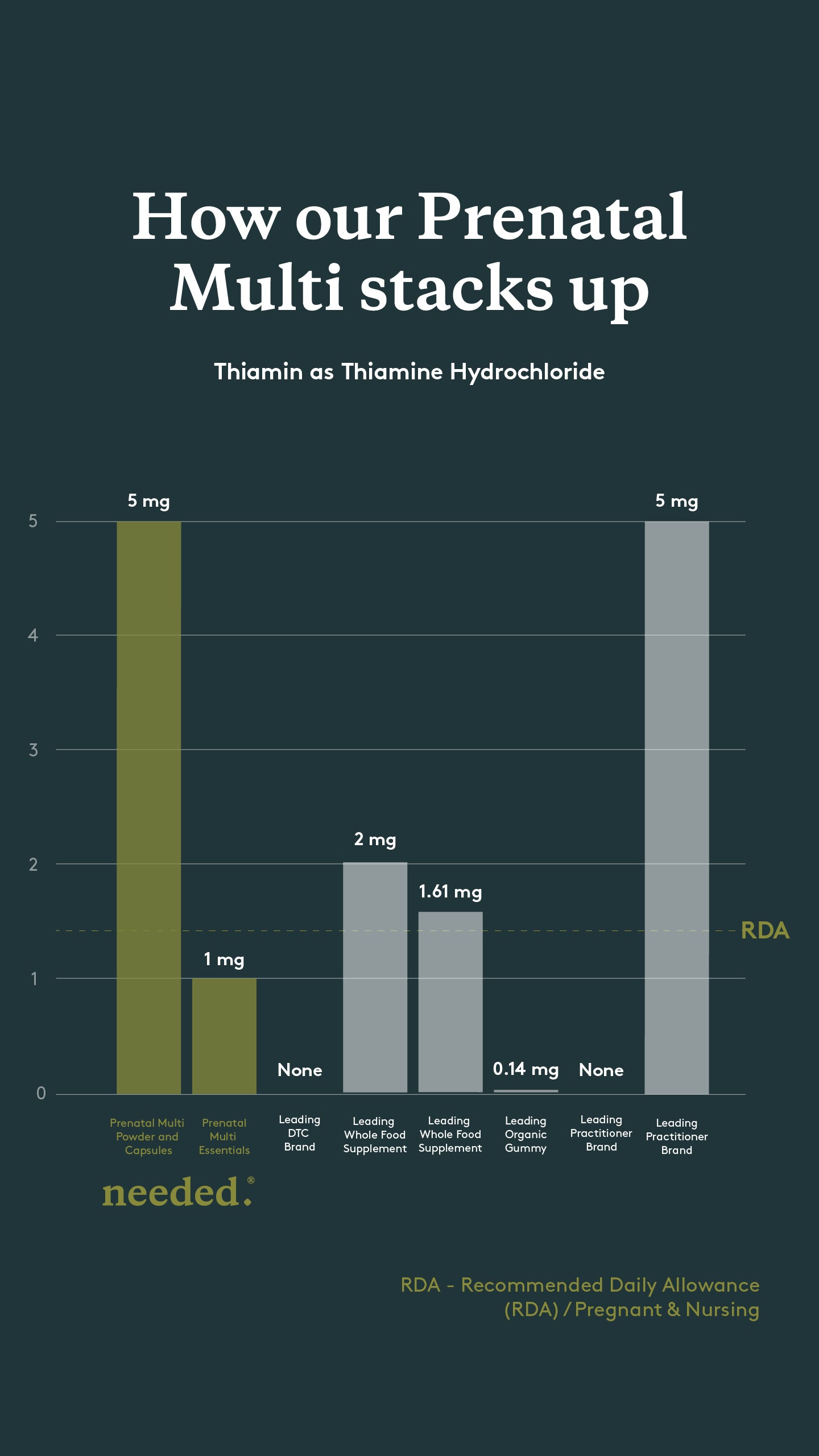
Thiamin (Vitamin B1)
as Thiamine HCI
5mg (Powder/Capsules) / 1mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- cardiovascular function
- energy generation
- managing stress levels
- carbohydrate metabolism
- healthy neurological function
How it supports baby:
- neurological development
- healthy cognitive function
- healthy cardiovascular function
- motor skill development
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
Thiamine deficiency may be driven by deficiencies in the soil & consumption of whole grain products.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Thiamin HCl is the most commonly used form of Thiamin in prenatal vitamins. Other forms of Thiamin may be better absorbed, but are not therapeutically indicated for pregnant women.
Why this dose?
Our dose provides enough to be effective, while still being safe for all mamas and mamas-to-be.

Additional information to note
Thiamine supplementation in pregnant women with prolonged vomiting should be initiated, to avoid development of Wernicke’s encephalopathy - a rare complication of hyperemesis gravidarum. Early thiamine replacement will reduce maternal morbidity and fetal loss rate.
Riboflavin (Vitamin B2)
as riboflavin 5-phosphate and riboflavin
20mg (Powder/Capsules) / 5mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- energy ATP production
- antioxidant involved in glutathione metabolism
- metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, fats
- healthy stress response
- healthy mood postpartum
- healthy immune and inflammatory response
How it supports baby:
- healthy growth and development
- energy (ATP) production
- healthy skin and mucous membranes
- healthy thyroid function
- normal heart development and function
- healthy immune and inflammatory response
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
Vegans, vegetarians & mamas with meat aversions can be deficient as it is primarily found in meat sources.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
The Riboflavin family are the precursors of the coenzymes, flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) and flavin mononucleotide (FMN). We use both forms to support production of both coenzymes as Riboflavin contributes the flavin to FAD and Riboflavin-5-Phosphate is synonymous to FMN.
Why this dose?
Despite being statistically rare in the USA, deficiency is observed in clinical practice, particularly in vegan and vegetarian mamas.


Niacin (Vitamin B3)
as niacinamide
25mg (Powder/Capsules) / 10mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- decreases likelihood of pre-eclampsia
- postpartum weight loss
- involved in cellular energy metabolism
- reduces inflammation and oxidative stress
- promoting healthy lipid profiles
- healthy skin
How it supports baby:
- fetal growth & development
- healthy skin
- promoting healthy birth weight and growth
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
Niacin is found in many animal proteins, but achieving optimal amounts through diet is difficult.
1 RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Niacinamide is the active form of Vitamin B3 and a component of NAD, a coenzyme that acts as an electron carrier in numerous reactions in the body.
Why this dose?
This dose is especially supportive for mamas on vegan or vegetarian diets, while being safe for all. Similar to Vitamin B3 dose in other prenatals and therapeutic to prevent deficiency, particularly in those on vegan or vegetarian diets.


Additional information to note
Niacin is the generic name for nicotinic acid, nicotinamide and niacinamide. Niacin in higher therapeutic doses can cause flushing, but Niacinamide does not have this effect. On labels, it is sometimes listed as Niacin Equivalent (NE) which is equal to 1 mg of Niacin.
Vitamin B6
as Pyridoxal-5-Phosphate
40mg (Powder/Capsules) / 15mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- minimizes nausea
- blood sugar balance
- healthy mood through production of several key neurotransmitters
-
increasing Magnesium absorption
-
protein utilization, by interconverting amino acids
How it supports baby:
-
DNA synthesis
- brain and nervous system development
- adequate birth weight
- healthy skin
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
58% of mamas have suboptimal blood levels at delivery, despite 75% meeting RDA through supplements
1 RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Pyridoxal-5-Phosphate is bioavailable and ready to be used by the body. It's only found in animal products. Many, due to a common genetic variation, are inefficient converters of B6 Pyridoxine into the active form.
Why this dose?
Our dose is especially supportive for mamas, including for mood imbalance and nausea, and is highly safe. Many mamas are low in B6, as hormonal birth control significantly depletes the body of it.


Folate
as L-Methylfolate
918 mcg DFE
(DFE, daily folate equivalents, standardizes the dose of Folate between the different forms as their absorption rates differ significantly)
How it supports mama:
- mood imbalances, as it helps produce several key neurotransmitters
- heart health
- healthy red blood cells
- immune support
- detoxification
How it supports baby:
- normal neural tube development
- normal midline development including the mouth
- DNA and red blood cell synthesis
- cell division, i.e. how baby grows
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
40% to 60% of women carry a gene variant that prevents the conversion of Folic Acid1
1 RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
We intentionally chose methylfolate over folic acid, as many women are unable to effectively utilize folic acid which needs multiple metabolic steps to convert it into its active form – methylfolate. Folate as methylfolate is bioavailable and ready to be used by the body without any metabolic road-blocks. Our dosage provides enough Folate to be effective, especially for those with conversion difficulty, while still being safe for all mothers and mothers-to-be.
Why this dose?
Our dose provides enough Folate to be effective, especially for those with conversion difficulty, while still being safe for all mamas and mamas-to-be. While too little Folate can lead to mood imbalances, so can too much Folate.


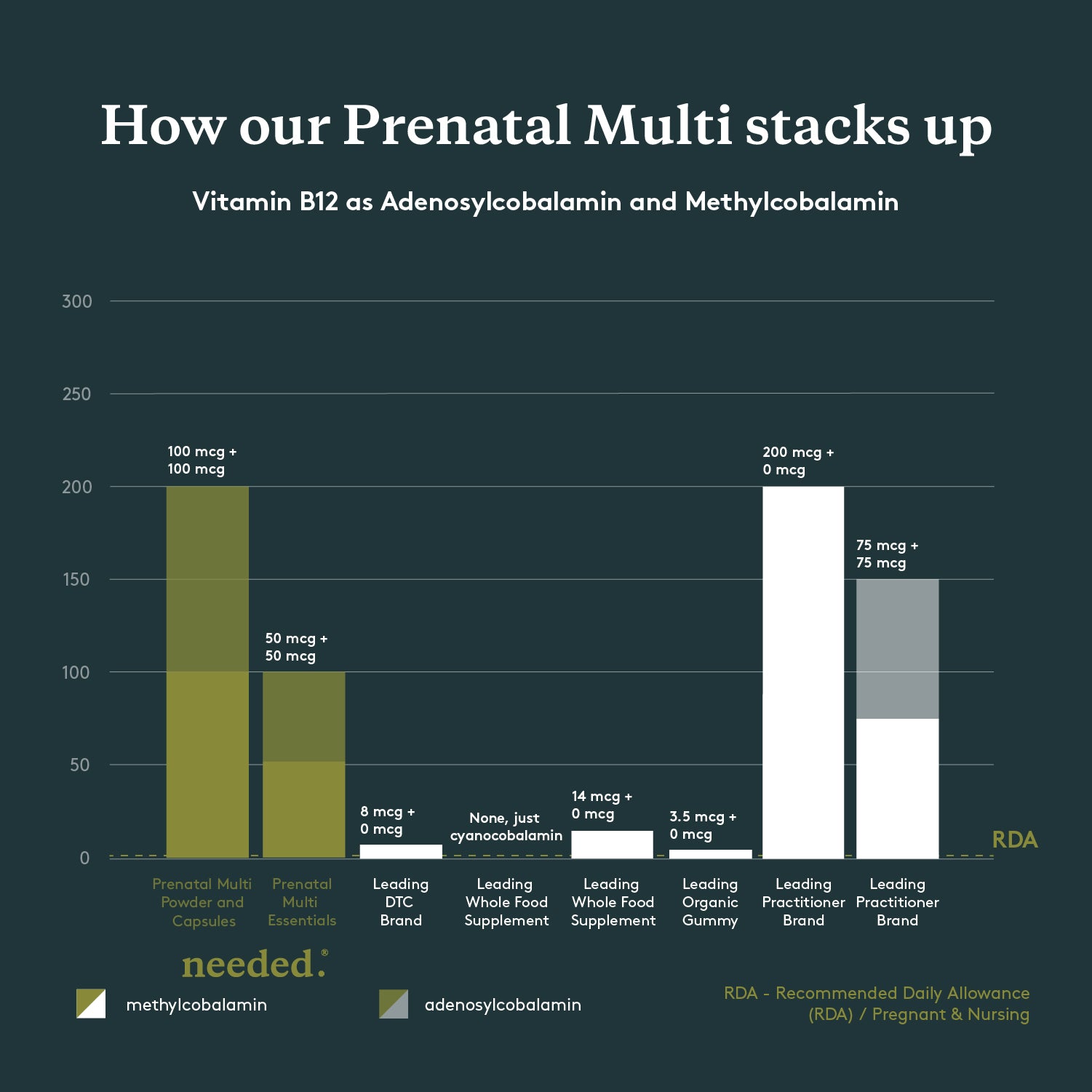
Vitamin B12
as 50% Adenosylcobalamin and 50% Methylcobalamin
200mcg (Powder/Capsules) / 100mcg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- energy levels
- healthy metabolism
- cognitive health
- managing stress
How it supports baby:
- DNA and red blood cell synthesis
- conduction of nerve impulses
- works synergistically with folate to support normal neural tube development
- cognitive development
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
The RDA for Vitamin B12 is grossly inadequate (by a 70x factor) and it’s difficult to get enough from food
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Methylcobalamin and Adenosylcobalamin are two active coenzyme forms that are readily usable by the body. Adenosylcobalamin specifically supports energy levels and a healthy metabolism, and is often missing in prenatals. Cyanocobalamin, the more common (cheap and man-made) form of B12, consists of Cobalamin (B12) attached to a cyanide molecule, a harmful compound that requires additional processing for safe removal from the body. We avoid this form.
Why this dose?
Our combination provides enough Vitamin B12 to be highly supportive, while still being safe for all mamas and mamas-to-be.

Additional information to note
Some mamas may need to supplement with additional B12. We considered a higher dose for this Prenatal Multi as it could benefit many mamas. However, a recent study has raised some questions about the safety of high doses of B12 in relation to risk of developing autism. This is likely due to 1) supplementation with Cyanocobalamin, which like Folic Acid, is thought to have a negative impact on methylation or 2) high unprocessed B12 levels can be a sign of chronic inflammation.
Biotin
350 mcg (Powder/Capsules) / 25mcg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- active in energy metabolism
-
cofactor for enzymes involved in many metabolic pathways
-
plays a role in fatty acid and carbohydrate metabolism
-
formation of keratin and development of epidermal cells and hair and nails, improving their condition
How it supports baby:
- essential for normal cell division and development
- essential component of many metabolic processes
- healthy skin, hair, eyes
- healthy gut and immune function
- healthy neurological function
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
An RDA does not exist because there is not enough evidence to suggest a daily amount needed by most healthy people.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Bioactive form used as a coenzyme for many metabolic reactions.
Why this dose?
Rapidly dividing fetal cells require Biotin so needs increase during pregnancy.
The body breaks down Biotin more rapidly during pregnancy and even marginal Biotin deficiency may be implicated in birth defects.


Additional information to note
Evidence suggest even marginal biotin deficiency may be teratogenic during pregnancy
Maternal alcohol intake can inhibit placental biotin transport to baby.
Pantothenic Acid
as calcium d-pantothenate
150mg (Powder/Capsules) / 10mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
-
cortisol (important stress hormone) and acetylcholine production (important neurotransmitter)
-
formation of coenzyme A, a metabolic cofactor for 100+ metabolic processes, including the production of cortisol, melatonin and acetylcholine
-
healthy sleep cycles
-
healthy cardiovascular function
-
supplementation in combination with Vitamin D supports a health microbiome
-
healthy immune response
How it supports baby:
-
supports healthy energy production, growth rates, and motor skills
-
promotes development of healthy gastrointestinal flora and GI health
-
supports healthy cardiovascular function
-
promotes a healthy immune response and sleep cycle
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
Deficiency is reported during pregnancy and lactation.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Most stable and bioactive form of pantothenic acid.
Why this dose?
Intake needs are increased during pregnancy and lactation, especially in those consuming lower calorie diets.


Additional information to note
Pantothenic acid is supplied in food and by the normal intestinal bacteria.
Choline
as Choline L(+) Bitartrate (VitaCholine™)
400mg (Powder/Capsules) / 150mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- healthy metabolism
- normal liver function
- efficient uptake of Omega-3 DHA
- memory and sleep-wake cycle function, due to its role in synthesizing the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine
- healthy cell membranes
- healthy blood pressure
How it supports baby:
- normal neural tube development
- optimal brain development, including cognitive performance
- proper DNA synthesis
- countering some of the adverse effects of prenatal stress
- transporting Omega-3 DHA from mama to baby
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
95%+ aren’t meeting their needs for Choline
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Choline Bitartrate is an optimal form for providing a concentrated dose that’s easily absorbed.
Why this dose?
Our Prenatal Multi Powder and Capsules plus our Prenatal Omega-3+ Vegan includes a combined dosage of 500mg of Choline. Some research suggests daily Choline intake above 900mg is optimal. 400-500mg of supplemental choline is optimal in a single serving. More choline can be taken at a different time of day to achieve a higher intake goal. We offer a Choline add-on for those that need it. On average, pregnant mamas consume just 320mg of Choline in their diet (eggs are the most common dietary source), so our dosage helps to fully fill in what's needed. Most prenatal vitamins contain only 0-55mg of Choline as it’s a bulky nutrient that can be difficult to formulate with.


Additional information to note
Choline’s RDA was not set until 1998, unlike most other nutrient RDAs that were established in 1941. RDAs are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy.
Vitamin K
As K2 menaquinone-7
90mcg (Powder/Capsules) / 45mcg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- bone health, especially with skeletal remodeling to prepare for birth
- blood sugar balance
- normal blood clotting
- a normal inflammatory response
- protecting skin elasticity
- utilizing Vitamin D3
How it supports baby:
- forming and strengthening bones and teeth
- cardiovascular health
- normal blood clotting
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
Vitamin K2 is not readily found in most foods. Our practitioners note high deficiency in clients.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Vitamin K2 as MK-7 (Menaquinone-7). MK-7 is found in fermented vegetables like natto and produced by healthy colonic bacteria. It lasts longer in the body than other forms of Vitamin K2.
Why this dose?
90mcg. This dose provides enough to be effective, while still being safe for all mamas and mamas-to-be.


Additional information to note
Newborns often receive Vitamin K1 injections because 1) very little transfers from mama to baby through the placenta, 2) breast milk has very tiny amounts, and 3) baby does not have enough bacteria in their colons to make Vitamin K2.
Calcium
as Di-Calcium Malate (DimaCal™) and naturally occurring
200mg (Powder/Capsules) / 100mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- healthy blood pressure
- cardiac function
- healthy bones
- production of hormones like insulin
- muscle relaxation
How it supports baby:
- forming and strengthening bones and teeth
- growing a healthy heart, nerves and muscles
- full-term gestation
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
Inadequate consumption of complementary nutrients: Vitamin D3, Vitamin K2, and Magnesium.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Di-Calcium Malate is absorbed significantly better than other forms of Calcium, such as Calcium Citrate or Carbonate.
Why this dose?
The RDA for Calcium is 1,000mg. However, Calcium is best taken throughout the day, rather than in a single large dose. And, too much Calcium at once can impact Iron absorption. So, we account for dietary intake of Calcium when setting our dose. Calcium is available in a wide variety of foods including broccoli, dark leafy greens, nuts, seeds, fish, and dairy. Plant based sources of Calcium are poorly absorbed. And, many fortified sources are not in the optimal form. Our dosage is supportive for filling in gaps in mama’s diet, especially if she is not consuming dairy products.


Additional information to note
Vitamin D, Vitamin K2, and Magnesium are required for your body to optimally process and utilize calcium. There is more often a shortage of D, K2, or Magnesium than Calcium.
Taking calcium can inhibit iron absorption by as much as 62%, but this depends on the dose of calcium. This interaction is of greatest concern for younger women, as they are the most likely to suffer iron deficiency.
Iodine
as potassium iodide
290mcg (Powder/Capsules) / 150mcg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- normal thyroid function
- pregnancy viability
- thyroid function
How it supports baby:
- brain development
- full-term gestation
- normal thyroid development
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
The need for Iodine is heightened during pregnancy and lactation.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Potassium Iodide is a well absorbed and reliable source of Iodine. Studies have found wide variations in the content of Iodine sourced from kelp.
Why this dose?
This matches the RDA for nursing women. Too little and too much Iodine is harmful. This dose provides enough to be effective, while still being safe for mamas and mamas-to-be that may be getting more from diet.


Additional information to note
Observational studies have shown associations between both mild maternal iodine deficiency and mild maternal thyroid hypofunction and decreased child cognition.
Magnesium
as Magnesium Bisglycinate
200mg (Powder/Capsules) / 100mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
-
healthy blood pressure
-
highly supportive for back pain, constipation, headaches, hypertension, impaired insulin metabolism, leg cramps, and nausea
-
promotes relaxation and improved sleep quality
How it supports baby:
-
formation of teeth and bones
-
adequate birth weight
-
DNA synthesis
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
50% of mamas don't meet the RDA
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Magnesium Glycinate, specifically Magnesium Bisglycinate, is a mineral chelate where the Magnesium is bound to two glycine amino acids. This form is better absorbed and gentler to digest than other forms of Magnesium. Some other forms, like Magnesium Oxide, can be so poorly absorbed that they can cause loose stools and inhibit the absorption of other nutrients.
Why this dose?
Most women are deficient, and baseline needs are elevated during pregnancy. Magnesium content in food is very low due to depletion from soil. And, it's a critical nutrient missing from most prenatals. We include a supportive dose of 200mg of Magnesium Bisglycinate, a gentle and well absorbed form. Our Hydration Support and Sleep + Relaxation Support provide additional Magnesium, if needed. We do not recommend taking more than 400mg at once, as higher dosages may slow the nutrient’s absorption.


Additional information to note
Additional Magnesium can be added at night to promote restful sleep.
Zinc
as Zinc Bisglycinate chelate (TRAACS™)
25mg (Powder/Capsules) / 15mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- immune function
-
protein synthesis
-
pregnancy viability
How it supports baby:
-
DNA snythesis
- cell division i.e. how baby grows
- adequate birth weight
-
full-term gestation
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
80% of pregnant women worldwide have inadequate zinc intake.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Zinc Bisglycinate. This chelated form of Zinc bound to Glycine is easily absorbed and gentle on the stomach.
Why this dose?
This dose provides enough to be effective, while still being safe for all mamas and mamas-to-be.


Additional information to note
Zinc supplementation along with copper helps balance absorption of both nutrients. Many alternative and integrative practitioners recommend a ratio of 15 mg of zinc to 1 mg of copper.Selenium
as Selenomethionine
200mcg (Powder/Capsules/Essentials)
How it supports mama:
- fertility and conception
- healthy thyroid function
How it supports baby:
-
healthy birth weight
-
full-term pregnancy
-
immune system development
-
healthy neurological development
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
Selenium levels are lower in pregnant women than in non-pregnant women.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Selenomethione is the most well-absorbed form of selenium.
Why this dose?
Selenium needs are significantly increased in pregnancy.


Copper
as copper bisglycinate chelate (TRAACS ™)
1mg (Powder/Capsules) / 0.5mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
-
healthy full-term pregnancy
-
promoting normal red and white blood cell profiles
-
healthy immune response
-
blood sugar balance
How it supports baby:
-
healthy fetal growth
-
energy production (ATP)
-
healthy gastrointestinal function
-
cognitive development
-
healthy immune response
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
Copper is an essential element required for the formation of many enzymes.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Bisglycinate chelates of copper are the most well-absorbed
Why this dose?
Copper needs are highest during pregnancy, but you don’t want too much as it competes with Zinc. A Zinc:Copper ratio of 25:1 is optimal.


Additional information to note
Copper is an important cofactor for many redox enzymes involved in numerous metabolic processes.
Manganese
as bisglycinate chelate (TRAACS ™)
5mg (Powder/Capsules) / 1mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
-
healthy full-term pregnancy
-
decreased risk for preeclampsia
-
cofactor for many enzymes involved in many metabolic processes
-
healthy immune response
-
normal blood clotting
How it supports baby:
-
healthy fetal bone growth
-
normal birth weight
-
cofactor for many enzymes involved in many metabolic processes
-
healthy immune response
-
normal blood clotting
-
healthy hair and skin
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
Manganese plays a significant role in female reproduction and fetal development.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Bisglycinate chelates are the most well-absorbed form.
Why this dose?
Provides adequate level to meet mama and baby’s requirements. Excessive Manganese is associated with maternal hypertension.


Additional information to note
Elevated manganese levels have been associated with hypertension and low birth weight in pregnancy.
Chromium
as Chromium Picolinate
120mcg (Powder/Capsules) / 45mcg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
-
healthy glucose homeostasis
-
healthy lipid profiles
-
may support healthy weight postpartum
How it supports baby:
- supports glucose homeostasis in preterm infants
- fetal facial feature development including eyes and ears
- thyroid function
- adequate birth weight
- full-term gestation
- healthy skin
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
Lactating women lose 50% more chromium in the urine than age-matched nonpregnant control women.
1 RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Chromium Picolinate is a well-absorbed and well-studied form.
Why this dose?
Mamas need higher intakes to due chromium losses during pregnancy and lactation.


Additional information to note
Pregnancy and Lactation typically drains chromium stores so supplementation is key.
Molybdenum
as molybdenum glycinate chelate (TRAACS ™)
100mcg (Powder/Capsules) / 10mcg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
-
healthy glucose homeostasis
-
cardiovascular health
-
activates metalloenzymes to breakdown toxins and sulfites
How it supports baby:
-
healthy glucose homeostasis in preterm infants
-
activates metalloenzymes to breakdown toxins and sulfites
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
Molybdenum is an essential trace nutrient in the human diet.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Glycinate mineral chelates are very well absorbed.
Why this dose?
Anyone following a dairy-free, grain-free, lentil, or bean-free diet may be deficient.


Additional information to note
Molybdenum cofactor deficiency is a very rare genetic condition in which babies are born without the ability to make molybdenum cofactor, which leads to brain abnormalities and developmental delays in early infancy.
Potassium
as Potassium Citrate
100mg (Powder/Capsules) / 0mg (Essentials)
How it supports mama:
-
helps prevent fluid accumulation in extremities
-
prevents electrolyte imbalance
-
healthy immune function
-
may help with restless legs or leg cramps
-
hormone balance
-
may help maintain normal blood pressure
How it supports baby:
-
healthy bone and muscle growth
-
optimal cellular function
-
organ and tissue health
-
healthy blood pressure
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
Potassium helps mama maintain proper electrolyte balance
1 RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Why this form?
Potassium Citrate is a well-absorbed form of potassium.
Why this dose?
Though potassium is readily available in foods, dietary surveys consistently show that people in the United States consume substantially less Potassium than recommended. This dose provides a bit of extra support, especially with blood volume expansion in pregnancy.


Additional information to note
High potassium (hyperkalemia) during pregnancy is dangerous and can lead to cardiovascular complications.
Boron
none
Most pregnant and nursing women aren’t meeting their baseline needs
Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) Pregnant & Nursing:
No RDA for Boron since an essential biological role for it has not been identified.
RDAs often provide far less nutrition than what you need. They are set by a government body with levels anchored by the minimum nutritional amounts necessary to avoid disease conditions, not to support you optimally before, during, and after pregnancy. Learn more here.
Additional information to note
Boron has been linked to helping make Vitamin D receptors more efficient, which is helpful. However, we already consume about a milligram of Boron daily, mostly from fruit and vegetables. And, we are otherwise unintentionally taking in Boron in drinking water or through other means as it is used regularly in glass, detergents, and agriculture. At high doses, Boron has been found to be a developmental and reproductive toxin in animals. For these reasons, we do not include Boron in our Prenatal Multi and suggest you avoid supplements that contain it.
Research Support
- Foods, fortificants, and supplements: Where do Americans get their nutrients? Journal of Nutrition.
- Periconceptional vitamin A use: how much is teratogenic? Reproductive Toxicology.
- Vitamin A in reproduction and development. Nutrients.
- Vitamin A and Pregnancy: A Narrative Review. Nutrients.
- The challenge to reach nutritional adequacy for vitamin A: β-carotene bioavailability and conversion--evidence in humans. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Research Support
- Regular vitamin C supplementation during pregnancy reduces hospitalization: outcomes of a Ugandan rural cohort study. Pan African Medical Journal.
- Influence of maternal nutrition on outcome of pregnancy: prospective cohort study. BMJ.
- Vitamin C supplementation in pregnancy. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.
- Immune-enhancing role of vitamin C and zinc and effect on clinical conditions. Annals of Nutrition & Metabolism.
- Selected vitamins and trace elements support immune function by strengthening epithelial barriers and cellular and humoral immune responses. British Journal of Nutrition.
- Effect of vitamin C on collagen structure of cardinal and uterosacral ligaments during pregnancy. European Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology and Reproductive Biology
- Interaction of vitamin C and iron. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
- Selected vitamins and trace elements support immune function by strengthening epithelial barriers and cellular and humoral immune responses. British Journal of Nutrition.
Research Support
- The Big Vitamin D Mistake.Journal of Preventive Medicine and Public Health
- Vitamin D supplementation during pregnancy: double-blind, randomized clinical trial of safety and effectiveness. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.
- Vitamin D supplementation, body weight and human serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D response: a systematic review. European Journal of Nutrition.
- High prevalence of vitamin D insufficiency in black and white pregnant women residing in the northern United States and their neonates. Journal of Nutrition.
- Maternal vitamin D status: effect on milk vitamin D content and vitamin D status of breastfeeding infants. Advanced Nutrition.
- The Effects of Vitamin D Supplement on Prevention of Recurrence of Preeclampsia in Pregnant Women with a History of Preeclampsia.
Research Support
- Vitamin E as an Antioxidant in Female Reproductive Health. Antioxidants (Basel)
- Vitamin E inadequacy in humans: causes and consequences. Advanced Nutrition.
- Distribution of serum concentrations of alpha-tocopherol and gamma-tocopherol in the US population. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
- Costa Rican adolescents have a deleterious nutritional profile as compared to adults in terms of lower dietary and plasma concentrations of antioxidant micronutrients. Journal of the American College of Nutrition.
- Plasma tocopherol and tocopherol to lipid ratios in a normal population of infants and children. International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research.
- Improved neurologic function after long-term correction of vitamin E deficiency in children with chronic cholestasis. New England Journal of Medicine.
- Antioxidant vitamin status during pregnancy in relation to cognitive development in the first two years of life. Early Human Development.
Research Support
- Dietary reference intakes for thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, folate, vitamin B12, pantothenic acid, biotin, and choline. National Academies Press.
- Enzymic evaluation of thiamin, riboflavin and pyridoxine status of parturient mothers and their newborn infants in a Mediterranean area of Spain. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
- B vitamins in breast milk: relative importance of maternal status and intake, and effects on infant status and function. Advanced Nutrition.
- Thiamine deficiency in infancy: long-term follow-up. Pediatric Neurology.
- Cardiac beriberi: often a missed diagnosis. Journal of Tropical Pediatrics.
Research Support
- B vitamins in breast milk: relative importance of maternal status and intake, and effects on infant status and function. Advanced Nutrition.
- Linus Pauling Institute - Oregon State University- Micronutrient Information Center - Riboflavin.
- Riboflavin: The Health Benefits of a Forgotten Natural Vitamin. International Journal of Molecular Sciences
- Immunomodulatory effect of riboflavin deficiency and enrichment-reversible pathological response versus silencing of inflammatory activation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences.
- Maternal intake of fat, riboflavin and nicotinamide and the risk of having offspring with congenital heart defects. European Journal of Nutrition.
Research Support
- National Institutes of Health - Office of Dietary Supplements - Niacin Fact Sheet For Health Professionals
- Maternal intake of fat, riboflavin and nicotinamide and the risk of having offspring with congenital heart defects. European Journal of Nutrition.
- Association between Vitamin Intake during Pregnancy and Risk of Small for Gestational Age. Nutrients.
- Vitamin B3 Nicotinamide: A Promising Candidate for Treating Preeclampsia and Improving Fetal Growth. The Tohoku Journal of Experimental Medicine.
Research Support
- Maternal intake of vitamin B6 and maternal and cord plasma levels of pyridoxal 5' phosphate in a cohort of Canadian pregnant women and newborn infants. The FASEB Journal.
- Vitamin B6 treatment of gestational diabetes mellitus: studies of blood glucose and plasma insulin. American Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology.
- Nausea and vomiting in pregnancy. New England Journal of Medicine.
- Genetics and genomics of human ageing. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society Biological Sciences.
Research Support
- Emphasis on folic acid And L-methylfolate. Reviews in Obstetrics and Gynecology.
- [6S]-5-methyltetrahydrofolate increases plasma folate more effectively than folic acid in women with the homozygous or wild-type 677C–>T polymorphism of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. British Journal of Pharmacology
- Is 5-methyltetrahydrofolate an alternative to folic acid for the prevention of neural tube defects? Journal of Perinatal Medicine.
- Unmetabolized folic acid is detected in nearly all serum samples from US children, adolescents, and adults. Journal of Nutrition.
- Folate, folic acid and 5-methyltetrahydrofolate are not the same thing. Xenobiotica.
- Recent Developments in Folate Nutrition. New Res Develop Water-Sol Vit.
Research Support
- Vitamin B-12 Status Differs among Pregnant, Lactating, and Control Women with Equivalent Nutrient Intakes. Journal of Nutrition.
- Vitamin B12 Metabolism and Status during Pregnancy, Lactation and Infancy. Nutrient Regulation during Pregnancy, Lactation, and Infant Growth. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology.
- The Coenzyme Forms of Vitamin B12: Toward an Understanding of their Therapeutic Potential. Alternative Medicine Review.
- The effects of vitamin B12 supplementation in pregnancy and postpartum on growth and neurodevelopment in early childhood: Study Protocol for a Randomized Placebo Controlled Trial. BMJ.
- Vitamin B12 supplementation during pregnancy and postpartum improves B12 status of both mothers and infants but vaccine response in mothers only: a randomized clinical trial in Bangladesh. European Journal of Nutrition.
- Vitamin B-12 supplementation during pregnancy and early lactation increases maternal, breast milk, and infant measures of vitamin B-12 status. Journal of Nutrition.
- Maternal Multivitamin Intake, Plasma Folate and Vitamin B12 Levels and Autism Spectrum Disorder Risk in Offspring. Paediatr Perinat Epidemiol.
Research Support
- Marginal biotin deficiency during normal pregnancy. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
- U.S. Department of Agriculture, Center for Nutrition Policy and Promotion Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
- Marginal biotin deficiency is common in normal human pregnancy and is highly teratogenic in the mouse.The Turkish Journal of Pediatrics.
- Inborn errors of biotin metabolism. Clinical and laboratory features of eight cases. Journal of Nutrition.
- Biotin. Advances of Nutrition Journal.
Research Support
- Pantothenic acid status of pregnant and lactating women. Journal of the American Dietetic Association.
- Coenzyme A, more than ‘just’ a metabolic cofactor. Biochemical Society Transactions.
- Effect of pantothenic acid deficiency of gastric secretion and motility. Journal of Clinical Investigation.
- Pantothenic acid deficiency induced in human subjects. Journal of Clinical Investigation
- Pantothenic acid. Monograph. Scientific Review of Alternative Medicine.
Research Support
- Pregnancy alters choline dynamics: results of a randomized trial using stable isotope methodology in pregnant and nonpregnant women. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
- Maternal choline intake alters the epigenetic state of fetal cortisol-regulating genes in humans. FASEB.
- A higher maternal choline intake among third-trimester pregnant women lowers placental and circulating concentrations of the antiangiogenic factor fms-like tyrosine kinase-1. FASEB.
- Choline intake during pregnancy and child cognition at age 7 years. American Journal of Epidemiology.
- Maternal choline supplementation during the third trimester of pregnancy improves infant information processing speed: a randomized, double-blind, controlled feeding study. FASEB.
- Choline: Exploring the Growing Science on Its Benefits for Moms and Babies. Nutrients.
- Choline and DHA in Maternal and Infant Nutrition: Synergistic Implications in Brain and Eye Health. Nutrients.
Research Support
- Oral Supplementation of Vitamin K for Pregnant Women and Effects on Levels of Plasma Vitamin K and PIVKA-II in the Neonate. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition.
- Usual Dietary Intake of Fermented Soybeans (Natto) Is Associated with Bone Mineral Density in Premenopausal Women. Journal of Nutritional Science and Vitaminology
- Bioavailability and Chemical/Functional Aspects of Synthetic MK-7 vs Fermentation-Derived MK-7 in Randomised Controlled Trials. International Journal for Vitamin and Nutrition Research
- Vitamin K2 Supplementation Improves Insulin Sensitivity via Osteocalcin Metabolism: A Placebo-Controlled. Trial Diabetes Care.
- Oral consumption of vitamin k2 for 8 weeks associated with increased maximal cardiac output during exercise. Alternative Therapies in Health and Medicine
- Maternal and Offspring Pools of Osteocalcin Influence Brain Development and Functions.
- Metabolism and cell biology of Vitamin K. Thrombosis Haemostasis
- Comparison of menaquinone-4 and menaquinone-7 bioavailability in healthy women. Nutrition Journal.
Research Support
- Calcium supplementation during pregnancy for preventing hypertensive disorders and related problems. Cochrane Database.
- Calcium: A Nutrient in Pregnancy. The Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India
- Hypertension in pregnancy: Role of body mass index, insulin resistance, aldosterone, and calcium homeostasis. Journal of Clinical Hypertension.
- Interventions for leg cramps in pregnancy. Cochrane Database.
- Calcium, magnesium and phosphorus in the nutrition of the newborn. Journal of the American College of Nutrition.
- Hypocalcemia in the Newborn. The Indian Journal of Pediatrics.
- Clinical Approach to Hypocalcemia in Newborn Period and Infancy: Who Should Be Treated? International Journal of Pediatric Otorhinolaryngology
Research Support
- Consequences of iodine deficiency and excess in pregnant women: an overview of current knowns and unknowns. American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
- The role of iodine in brain development. Proceedings of the Nutrition Society
- The implications of iodine and its supplementation during pregnancy in fetal brain development. Current Clinical Pharmacology
- National Institutes of Health - Office of Dietary Supplement - Iodine Fact Sheet for Health Professionals
- Iodine in Pregnancy: Is Salt Iodization Enough? The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism.
- The Cognitive Effects of Micronutrient Deficiency: Evidence from Salt Iodization in the United States. Journal of the European Economic Association
Research Support
- Effect of Magnesium Supplement on Pregnancy Outcomes: A Randomized Control Trial - 2017 Adv Biomed Res
- Bioavailability of magnesium diglycinate vs magnesium oxide in patients with ileal resection. Journal of Parenteral and Enteral Nutrition.
- Magnesium in pregnancy blood pressure and pre-eclampsia - A review.Pregnancy Hypertension Journal.
- Oral magnesium for relief in pregnancy-induced leg cramps: a randomised controlled trial. Maternal & Child Nutrition.
Research Support
- Effect of zinc supplementation on pregnancy and infant outcomes: a systematic review. Paediatric and Perinatal Epidemiology.
- Zinc supplementation for improving pregnancy and infant outcome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews.
- Selenium, Zinc, and Manganese Status in Pregnant Women and Its Relation to Maternal and Child Complications. Nutrients.
- Zinc supplementation for improving pregnancy and infant outcome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
- National Institutes of Health - Office of Dietary Supplement - Zinc Fact Sheet for Health Professionals
- Zinc and infant nutrition. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics
Research Support
- Selenium supplementation in the management of thyroid autoimmunity during pregnancy: results of the "SERENA study", a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Endocrine.
- Selenium, Zinc, and Manganese Status in Pregnant Women and Its Relation to Maternal and Child Complications. Nutrients.
- National Institutes of Health - Office of Dietary Supplement - Selenium Fact Sheet for Health Professionals
- The role of selenium in human conception and pregnancy. Journal of Trace Elements in Medicine and Biology
- Recurrent spontaneous abortion and selenium deficiency. International Journal of Gynecology & Obstetrics
Research Support
- National Institutes of Health - Office of Dietary Supplement - Copper Fact Sheet for Health Professionals
- Maternal plasma concentrations of magnesium, calcium, zinc and copper in normal and pathological pregnancies. Science of the Total Environment.
- Serum zinc and copper concentrations in maternal and umbilical cord blood. Relation to course and outcome of pregnancy. Scandinavian Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Investigation.
- Copper homeostasis in infant nutrition: deficit and excess. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology and Nutrition.
- Clinical manifestations of nutritional copper deficiency in infants and children. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
- Copper and immunity. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
Research Support
- Manganese and birth outcome. Nutrition Reviews.
- Manganese concentrations in maternal–infant blood and birth weight. Environmental Science and Pollution Research.
- The Essential Element Manganese, Oxidative Stress, and Metabolic Diseases: Links and Interactions. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity.
- Nutritional aspects of manganese homeostasis. Molecular Aspects of Medicine.
- The role of nutrients in bone health, from A to Z. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.
Research Support
- Essentiality of chromium in humans. Science of the Total Environment.
- Chromium supplementation of human subjects: Effects on glucose, insulin and lipid parameters. Metabolism.
- Chromium in human milk from American mothers. British Journal of Nutrition.
- National Institutes of Health - Office of Dietary Supplement - Chromium Fact Sheet for Health Professionals.
- Effects of Chromium on Glucose Tolerance in Infants Receiving Parenteral Nutrition Therapy. Nutrition in Clinical Practice.
Research Support
- A novel treatment for “morning sickness”: Nausea of pregnancy could be induced by excess sulfite which molybdenum can help alleviate.Medical Hypotheses.
- A prospective study of early pregnancy essential metalloids and glucose levels late in the second trimester. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism.
- A Turkish Case with Molybdenum Cofactor Deficiency. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids.
- National Institutes of Health - Office of Dietary Supplement - Molybdenum Fact Sheet for Health Professionals.



